Can RDS Scale Up On Schedule? Automating for Predictable Workloads
 EventBridge for timing and Lambda for execution to build an automated, time-based workflow. This allows you to proactively match your database resources to known traffic patterns, optimizing for both cost and performance.
EventBridge for timing and Lambda for execution to build an automated, time-based workflow. This allows you to proactively match your database resources to known traffic patterns, optimizing for both cost and performance.
Stop wasting money on idle non-production RDS instances. Server Scheduler provides an easy, no-code solution to automate start, stop, and resize schedules, cutting your AWS bill by up to 70%. Discover a simpler way to automate your AWS costs.
Contents
Ready to Slash Your AWS Costs?
Stop paying for idle resources. Server Scheduler automatically turns off your non-production servers when you're not using them.
Understanding Native RDS Autoscaling vs. Scheduled Scaling
Before building a custom solution, it's critical to understand what Amazon RDS handles out of the box. Many teams hear "autoscaling" and assume it covers all performance and cost needs, but the native RDS feature is much more limited. This misconception can lead to unexpected performance bottlenecks and inflated bills if not properly understood. The built-in feature, Storage Autoscaling, is purely a safety net designed to prevent your database from running out of disk space. When free storage drops below a certain threshold, it automatically allocates more disk space to keep your application online.
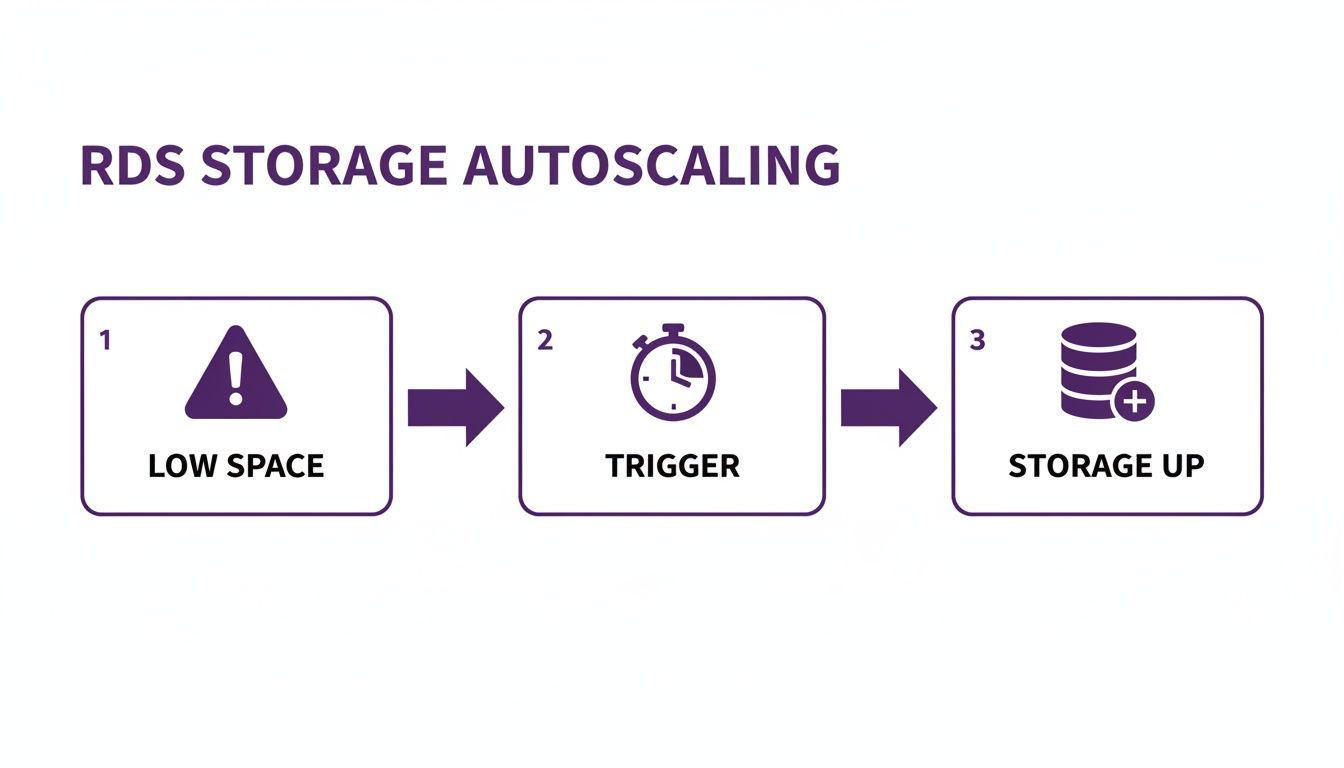
However, this native feature has significant limitations. It only scales storage, not compute resources like CPU or memory. If your application faces a traffic spike, Storage Autoscaling will do nothing to help. Furthermore, it's a one-way street; it only scales up and never scales down. A temporary data import could trigger a permanent storage increase, leaving you paying for unused capacity indefinitely. The official AWS documentation confirms this, making it an unsuitable tool for dynamic cost management. True scheduled scaling involves changing the DB instance class (e.g., from db.t3.medium to db.m5.xlarge) to handle predictable changes in demand.
Key Takeaway: Native RDS Storage Autoscaling is a reactive safety net for disk space, not a proactive strategy for managing performance or cost. To align compute resources (CPU/RAM) with predictable workloads, you must implement a custom scheduled scaling solution.
How to Build Your Own RDS Scaling Schedule
Since Amazon RDS lacks a native scheduler for instance resizing, you must create your own. The most common method combines two powerful serverless tools: Amazon EventBridge and AWS Lambda. EventBridge acts as the cron-based timer, triggering your scaling actions on a predefined schedule, while a Lambda function contains the logic to execute the resize. This approach is reliable, cost-effective, and highly customizable. You typically create two separate EventBridge rules: one to scale up before a high-traffic period and another to scale down afterward.
For example, a cron expression like cron(0 8 ? * MON-FRI *) can trigger an event at 8:00 AM UTC every weekday. When the rule fires, it invokes your Lambda function. This function uses the AWS SDK to call the ModifyDBInstance API action, specifying the target database and the new instance class. Proper implementation also requires careful attention to IAM permissions. Your Lambda function needs an IAM role with rds:ModifyDBInstance permissions, scoped tightly to the specific RDS instances you intend to scale to follow the principle of least privilege.
The ModifyDBInstance API call includes a critical boolean parameter, ApplyImmediately. Setting this to true applies the change right away, which causes a brief reboot and downtime. This is necessary for scheduled scaling to ensure resources are ready for a predictable peak. If set to false, the change is queued for the next maintenance window, defeating the purpose of time-based scaling. Therefore, you should always schedule the event during a period when a few minutes of downtime is acceptable. Ready to stop wasting money on idle RDS instances? Our guide on how to schedule AWS RDS to stop and start provides a clear, actionable plan to significantly cut your cloud costs.
Practical Use Cases for Scheduled RDS Scaling
Scheduled scaling is not just a technical exercise; it's a powerful strategy for saving money and preventing performance issues in common business scenarios. Two of the most impactful use cases are optimizing non-production environments and preparing for predictable traffic spikes. Development, staging, and QA environments are often a major source of wasted cloud spend. They are critical during the 40-hour work week but sit completely idle for the other 128 hours on nights and weekends, racking up costs for no reason.
By scheduling these instances to scale down to a minimal size (or stop entirely) outside of business hours, you can slash their costs by over 60%. Similarly, applications with cyclical demand, like an e-commerce site with a weekly flash sale or an analytics platform running a nightly ETL job, benefit immensely. Instead of provisioning for peak capacity 24/7, you can schedule the database to scale up just before the demand hits and scale back down immediately after. This ensures flawless performance when it matters most without paying for idle capacity the rest of the day. This proactive approach is a cornerstone of smart cloud financial management, as highlighted in this analysis of AWS scaling services.
Moving Beyond DIY Scripts with an Automation Platform
While the DIY approach with EventBridge and Lambda is effective, it comes with significant overhead. It requires engineering time to write, test, and maintain code, manage IAM roles, and handle complexities like time zones and API updates. For many organizations, this maintenance burden becomes a distraction from core business objectives. As you scale, managing dozens of individual scripts becomes an operational nightmare, lacking centralized visibility and governance.
A dedicated automation platform like Server Scheduler is the logical next step. These tools replace custom code with a simple, visual interface, allowing both engineers and non-technical staff to create and manage scaling schedules in minutes. This not only accelerates implementation but also democratizes cost optimization. By using a managed service, you offload the maintenance of the underlying infrastructure and ensure your automation stays up-to-date with AWS changes. You gain a centralized dashboard to enforce policies, audit changes, and track the financial impact of your optimizations across the entire organization. This strategic shift from scattered scripts to a unified platform brings predictability and control to your cloud cost management efforts. To learn more about this approach, explore different cloud cost optimization tools.
Common Questions About Scheduling RDS Scaling
When implementing scheduled RDS scaling, a few key questions almost always arise. Understanding the answers is crucial for a smooth and predictable process. The most important question is whether the database will experience downtime during scaling. The answer is yes, but the duration depends on your configuration. A standard single-AZ instance will reboot to apply the change, causing a few minutes of downtime.
However, a Multi-AZ setup handles this more gracefully. AWS applies the change to the standby instance first, then initiates a failover, reducing the interruption to just 60-120 seconds. Regardless of the setup, it is always best practice to schedule scaling events during a low-traffic window. Another common concern is the impact on backups. Automated backups and snapshots are managed separately and are not interrupted by scaling. However, to avoid conflicts, you should schedule scaling activities outside of your defined backup and maintenance windows. Finally, it's important to note that this type of scheduled scaling does not apply to Aurora Serverless, which scales automatically based on live workload rather than a fixed schedule.
Ready to stop overpaying for idle RDS instances? With Server Scheduler, you can easily automate start, stop, and resize schedules to slash your AWS bill by up to 70%. Try it now and see how much you can save.