Top 12 Cloud Infrastructure Automation Tools for 2026

In the complex world of cloud computing, manual infrastructure management is no longer a viable option. It's slow, error-prone, and inefficient, leading to configuration drift, security vulnerabilities, and runaway costs. The solution lies in adopting the right cloud infrastructure automation tools, which enable teams to define, deploy, and manage resources programmatically through an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) approach. This shift empowers DevOps and platform engineers to build scalable, resilient, and cost-effective systems with unprecedented speed and consistency.
Ready to slash your cloud costs? While IaC tools build your infrastructure, Server Scheduler automates stopping and starting non-production resources to cut your AWS bill by up to 70%. Start your free trial today!
This comprehensive guide is designed to help you navigate the crowded market of automation solutions. We will cut through the marketing noise to provide a detailed, practical analysis of the leading platforms. You will find a categorized roundup covering everything from provisioning and configuration management to CI/CD and cost optimization. Each entry includes a concise feature summary, ideal use cases, a frank assessment of pros and cons, and key integration notes to help you understand how these tools fit into a broader ecosystem. For instance, while provisioning tools set up your infrastructure, a solution like Server Scheduler can complement them by automating start/stop schedules for non-production environments to drastically reduce AWS costs.
Our goal is to equip you with the information needed to make an informed decision. We will also explore how security must be a core component of your automation strategy; integrating automated cloud security assessment tools from the beginning is critical to prevent misconfigurations that could expose your infrastructure. This article provides direct links and focused analysis to help you select the best cloud infrastructure automation tools for your specific technical and business requirements.
Contents
- 1. Server Scheduler
- 2. AWS Marketplace – Infrastructure as Code category
- 3. HashiCorp Terraform (HCP Terraform / Terraform Enterprise)
- 4. Pulumi
- 5. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- 6. Spacelift
- 7. env0
- 8. Scalr
- 9. AWS Systems Manager Automation (Runbooks)
- 10. AWS CloudFormation
- 11. Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager (Infra Manager)
- 12. Azure Bicep (and ARM Templates) – Microsoft
- Cloud Infrastructure Automation — 12-Tool Comparison
- Final Thoughts
Ready to Slash Your AWS Costs?
Stop paying for idle resources. Server Scheduler automatically turns off your non-production servers when you're not using them.
1. Server Scheduler
Server Scheduler stands out as a powerful and highly accessible cloud infrastructure automation tool, specifically engineered for cost optimization and operational efficiency. Instead of requiring complex scripts or deep Infrastructure as Code (IaC) knowledge, it provides a simple, point-and-click visual interface for managing resource schedules. This approach makes it an ideal solution for DevOps, FinOps, and platform teams aiming to achieve significant cost savings without a steep learning curve.
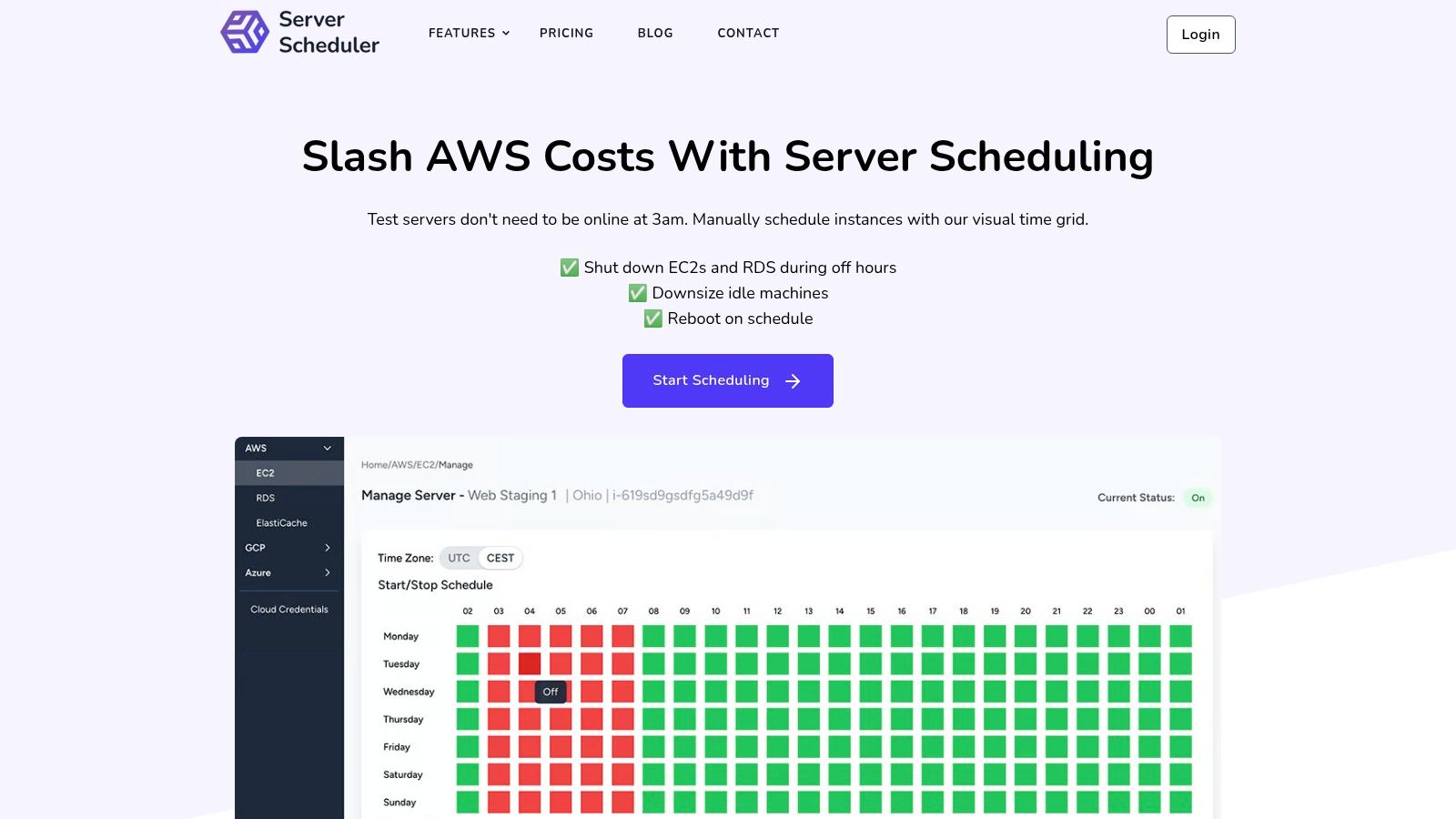
The platform’s core strength lies in its ability to automate the start/stop, resize, and reboot cycles of AWS resources like EC2, RDS, and ElastiCache. By powering down non-production environments during nights and weekends, teams can cut cloud bills by up to 70%. Its visual time grid, complete with localized time zones, simplifies creating complex schedules that would otherwise demand meticulous management of Linux task scheduling with cron jobs. For instance, teams can automatically scale up compute resources for peak business hours and scale them down during lulls, ensuring performance without overspending. You can learn more about its EC2 start/stop scheduling capabilities to see how this works in practice.
Key Features: Cost Optimization, Operational Scheduling, User-Friendly Interface, Multi-Account Management.
While currently focused on AWS, its roadmap includes Google Cloud and Azure, positioning it as a future multi-cloud solution. The transparent monthly pricing (€49/mo Standard, €99/mo Advanced) and quick setup process make Server Scheduler a compelling choice for teams seeking fast, tangible results from their cloud automation efforts. However, teams needing enterprise-grade features like SSO or RBAC should note these are not currently listed.
2. AWS Marketplace – Infrastructure as Code category
For teams deeply embedded in the Amazon Web Services ecosystem, the AWS Marketplace serves as a centralized hub for discovering, procuring, and deploying essential cloud infrastructure automation tools. Rather than navigating countless vendor websites, this curated category offers a streamlined experience. It simplifies finding and purchasing commercial and open-source Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) solutions, from configuration management platforms to specialized CI/CD services.
The primary advantage of the AWS Marketplace is its tight integration with AWS accounts. Procurement is simplified through consolidated billing, meaning software purchases appear directly on your monthly AWS bill. This is a significant benefit for enterprise finance and procurement teams. Additionally, the platform supports private offers, allowing for negotiated pricing and terms directly with vendors. The listings are vetted for AWS compatibility, available as AMIs, containers, or SaaS subscriptions, which removes guesswork during implementation. However, its strength is also its limitation: the platform is almost exclusively focused on tools that run on or integrate with AWS. For a closer look at managing expenses on the platform, explore these cloud cost optimization tools.
3. HashiCorp Terraform (HCP Terraform / Terraform Enterprise)
HashiCorp Terraform has become the de facto industry standard for provisioning and managing infrastructure using a declarative approach. As one of the most essential cloud infrastructure automation tools, it enables teams to define both cloud and on-prem resources in human-readable configuration files. While the open-source version is powerful, HashiCorp offers commercial versions like HCP Terraform (SaaS) and Terraform Enterprise (self-managed) to address governance, collaboration, and security at scale.
Terraform's primary advantage is its provider-based, platform-agnostic architecture. With a massive ecosystem of official, partner, and community-developed providers, it can manage a diverse range of services well beyond the major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP. The commercial offerings add critical enterprise features like remote state management, run triggers for complex workflows, private module registries for sharing reusable code securely, and Sentinel for policy-as-code enforcement. Terraform excels at orchestrating complex, multi-cloud deployments from a single, unified workflow. However, mastering its state management and structuring reusable modules requires a significant learning investment. Integrating its lifecycle with cost management is crucial; effective FinOps best practices ensure that provisioned infrastructure aligns with budget forecasts.
4. Pulumi
Pulumi empowers developers to define and manage cloud infrastructure using familiar, general-purpose programming languages like TypeScript, Python, and Go. This approach shifts Infrastructure as Code (IaC) from domain-specific languages (DSLs) to the same tooling and practices used for application development. The core of its offering is an open-source SDK, complemented by the Pulumi Cloud platform, which provides essential collaboration and governance features for teams.
Pulumi's main draw is its developer-centric philosophy. It allows engineering teams to leverage existing skills, libraries, and testing frameworks to build reliable infrastructure. Instead of learning a new syntax, developers can use loops, functions, and classes to create reusable and testable infrastructure components. Pulumi Cloud enhances this with features like state management, role-based access control (RBAC), and policy-as-code to ensure security and compliance across deployments. In practice, teams adopt Pulumi to unify application and infrastructure codebases, streamlining CI/CD pipelines. Its Automation API enables programmatic control over deployments, making it a powerful tool for building custom platforms. While the free tier is excellent for individuals, teams must plan for the metered resource pricing of Pulumi Cloud.
5. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform extends the popular open-source Ansible project into a full-fledged enterprise solution for managing complex, hybrid-cloud environments. It combines the simplicity of YAML-based playbooks with powerful tools for control, governance, and analytics. This makes it one of the most versatile cloud infrastructure automation tools for teams that need to orchestrate everything from initial server provisioning to ongoing application configuration and day-two operational tasks.
The platform's core strength lies in its comprehensive, agentless approach and enterprise-grade features. Components like the Automation Controller (formerly Tower) provide a centralized UI for managing job scheduling, credentials, and role-based access control. The included Automation Hub serves as a private repository for certified, trusted content collections from Red Hat and its partners, ensuring quality and security. This ecosystem provides a reliable foundation for scaling automation across an organization. Ansible is exceptionally well-suited for configuration management and executing operational runbooks, such as patching servers or performing application deployments. It can automate routine VM actions like starting or stopping instances, which is a key cost-saving measure. For a deeper dive into these instance lifecycle actions, you can learn more about EC2 stop, start, and reboot operations.
6. Spacelift
Spacelift is a sophisticated CI/CD and orchestration platform designed specifically for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) workflows. It goes beyond simple automation by providing a robust framework for governance, security, and compliance, making it one of the more powerful cloud infrastructure automation tools for enterprises. It supports a wide range of IaC technologies, including Terraform, OpenTofu, CloudFormation, Pulumi, and Ansible, allowing teams to manage diverse stacks from a single control plane.
The platform’s key differentiator is its emphasis on Policy-as-Code, utilizing Open Policy Agent (OPA) to enforce granular controls over infrastructure changes. This allows organizations to implement security guardrails, cost controls, and compliance checks automatically within the deployment pipeline. Spacelift’s flexible architecture, offering both SaaS and self-hosted models (including air-gapped and FedRAMP-authorized options), makes it suitable for highly regulated industries like finance and government. Teams use Spacelift to create multi-stage IaC pipelines that integrate directly with version control systems, automating everything from planning to deployment. Its drift detection feature continuously monitors infrastructure for unauthorized changes and can trigger automated remediation workflows.
7. env0
For teams leveraging Infrastructure as Code frameworks like Terraform, OpenTofu, or Pulumi, env0 acts as a centralized management and governance layer. It extends basic IaC capabilities with a focus on self-service, cost control, and policy enforcement. This platform is one of the more specialized cloud infrastructure automation tools, designed to help platform and FinOps teams streamline environment provisioning while maintaining strict operational guardrails.
env0’s primary strength lies in its ability to manage the entire lifecycle of a cloud environment. It integrates powerful GitOps workflows, enabling automated provisioning triggered by pull requests and commits. Crucially, it adds features like environment Time-to-Live (TTL) and schedule-based deployments, which automatically decommission resources to prevent unnecessary cloud spend. This makes it particularly valuable for managing temporary development, staging, or QA environments. The platform provides robust drift detection, not only identifying discrepancies between code and the live environment but also suggesting remediation paths. Its integration with cost estimation tools like Infracost gives developers visibility into the financial impact of their infrastructure changes before they are applied.
8. Scalr
Scalr offers a compelling alternative in the Terraform automation space, focusing on enterprise governance and a unique, usage-based pricing model. Positioned as a direct competitor to Terraform Cloud and other CI/CD platforms, it provides a SaaS solution for managing Terraform and OpenTofu workflows. Its key differentiator is a billing structure tied to the number of infrastructure runs, not the number of users or concurrent operations, making it an attractive option for large or growing teams.
The primary appeal of Scalr is its transparent, per-run pricing model. This approach eliminates the licensing complexity and cost penalties associated with adding more engineers to a project, which can be a significant hurdle with per-seat licenses. By including private agents and policy-as-code features (using Open Policy Agent) without extra fees, Scalr simplifies budgeting and encourages broader team collaboration on infrastructure management. This makes it one of the more financially predictable cloud infrastructure automation tools for organizations with high user counts but variable deployment frequencies. Scalr is well-suited for enterprises seeking robust governance features like SAML support, drift detection, and cost estimation directly within their IaC pipeline.
9. AWS Systems Manager Automation (Runbooks)
For organizations heavily invested in AWS, Systems Manager Automation provides a native service to codify and automate operational procedures as cloud infrastructure automation tools called "runbooks." It streamlines common and repetitive IT tasks, such as starting and stopping instances, applying patches, or resizing resources across multiple AWS accounts and Regions. By translating manual processes into reliable, repeatable code, it significantly reduces the potential for human error.
The primary advantage is its deep, first-class integration with the AWS ecosystem. Automation runbooks have direct, secure access to AWS APIs, enabling powerful actions without managing complex credentials. The service includes a library of pre-built runbooks from AWS for common tasks, while also allowing teams to create custom runbooks using Python or PowerShell scripts. This flexibility makes it a powerful tool for enforcing operational best practices and compliance at scale. Systems Manager Automation excels at event-driven and scheduled actions. When integrated with Amazon EventBridge, it can trigger runbooks based on specific events or on a recurring schedule. For specific tasks like instance modifications, you can learn how to resize an EC2 instance using these automated workflows.
10. AWS CloudFormation
For organizations committed to the Amazon Web Services ecosystem, AWS CloudFormation is the foundational service for modeling, provisioning, and managing cloud resources as code. As a native Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) offering, it provides a common language to describe and provision all the infrastructure resources in your cloud environment. This service allows you to use declarative templates written in YAML or JSON to automate the setup of everything from a simple S3 bucket to complex, multi-tier application stacks, ensuring your cloud infrastructure automation tools are deeply integrated with the platform itself.
CloudFormation’s primary strength is its unparalleled integration with AWS services. New features and resource types are typically supported on day one, providing a level of reliability and consistency that third-party tools can struggle to match. Its concept of "stacks" treats a collection of resources as a single unit, which can be created, updated, or deleted together, simplifying lifecycle management. Features like Change Sets allow you to preview the impact of template modifications before execution, preventing unintended changes to your production environments. The service is highly effective for automating repeatable deployments and ensuring architectural consistency across different environments (dev, staging, prod).
11. Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager (Infra Manager)
For teams building on Google Cloud, Infrastructure Manager provides a managed service to automate the deployment and management of Terraform configurations. This tool simplifies IaC by using Google-managed execution engines like Cloud Build and storing state files securely in Cloud Storage. It serves as one of the core cloud infrastructure automation tools within the GCP ecosystem, abstracting away the operational overhead of running Terraform at scale.
The primary appeal of Infra Manager is its native integration and managed execution model. Teams can apply configurations without setting up their own CI/CD pipelines or state-locking mechanisms, as Google handles the underlying workflows. It integrates directly with GCP Service Catalog and Marketplace, allowing organizations to create and distribute pre-approved infrastructure blueprints and solutions, ensuring consistency and governance across projects. This centralizes control while empowering development teams. Using Infra Manager involves defining deployments based on Terraform configurations stored in sources like Cloud Git repositories or Cloud Storage buckets. The service then orchestrates the deployment process using Google's reliable infrastructure.
12. Azure Bicep (and ARM Templates) – Microsoft
For organizations committed to the Microsoft Azure ecosystem, Azure Bicep offers a modern, domain-specific language (DSL) for declarative infrastructure deployment. As a transparent abstraction over Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates, Bicep simplifies the authoring experience with a cleaner syntax, improved type safety, and modularity. It is one of the most direct and powerful cloud infrastructure automation tools for managing resources natively within Azure.
The key advantage of Bicep is its day-zero support for all Azure services and features. Because it compiles directly to ARM JSON, any new Azure resource or API version is immediately available, eliminating the lag often seen with third-party tools. Bicep is free, open source, and fully supported by Microsoft, with first-class tooling integrated directly into VS Code and the Azure CLI. This native integration ensures a seamless and highly reliable deployment experience without external state management dependencies. Bicep excels at orchestrating complex Azure environments, from networking and compute to data and identity services. Its "what-if" deployment feature allows teams to preview changes before applying them, reducing the risk of misconfiguration.
Cloud Infrastructure Automation — 12-Tool Comparison
| Product | Core features | UX / Quality | Value & Price | Target audience & USP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🏆 Server Scheduler | Start/stop, resize, reboot (EC2/RDS/ElastiCache); visual time grid; localized time zones | ★★★★★ — point‑and‑click, audit logs | 💰 Standard €49/mo; Advanced €99/mo — claims up to 70% savings | 👥 DevOps / FinOps / SMEs — ✨ visual scheduler, fast ROI, multi‑account |
| AWS Marketplace – Infrastructure as Code category | Curated IaC listings, consolidated billing, filters | ★★★★ — easy discovery & procurement | 💰 Vendor pricing varies; consolidated billing & private offers | 👥 IT procurement & enterprises — ✨ billing + marketplace discovery |
| HashiCorp Terraform (HCP/Enterprise) | Declarative multi‑cloud provisioning, providers, remote state, policy | ★★★★☆ — broad community & tooling | 💰 OSS free; HCP/Enterprise paid tiers | 👥 Platform teams & enterprises — ✨ massive ecosystem & governance |
| Pulumi | Multi‑language IaC (TS/Python/Go/C#), Pulumi Cloud (state, policies) | ★★★★ — developer‑friendly, CI/CD friendly | 💰 Free personal tier; metered team pricing | 👥 Developers & cloud teams — ✨ use real programming languages |
| Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform | Playbooks, controller, Automation Hub, certified collections | ★★★★ — enterprise runbooks & analytics | 💰 Subscription (contact sales) | 👥 Ops & enterprise teams — ✨ certified content + enterprise support |
| Spacelift | Multi‑IaC pipelines, policy‑as‑code, drift detection, SaaS/self‑hosted | ★★★★ — governance & security focused | 💰 Contact sales; FedRAMP options for public sector | 👥 Regulated enterprises & platform teams — ✨ FedRAMP & multi‑IaC orchestration |
| env0 | GitOps provisioning, environment TTL/scheduling, drift & cost controls | ★★★★ — strong cost/visibility tooling | 💰 Tiered pricing; higher tiers via quote | 👥 Platform & FinOps teams — ✨ environment scheduling & Infracost integration |
| Scalr | Usage‑based per‑run billing, private agents, policy checks, drift detection | ★★★★ — transparent billing for large teams | 💰 Usage‑based (per run); no per‑user fees | 👥 Large teams & cost‑sensitive orgs — ✨ per‑run model + private agents |
| AWS Systems Manager Automation (Runbooks) | Automation runbooks, EventBridge scheduling, IAM auditing | ★★★★ — deep AWS integration & auditing | 💰 Pay‑as‑you‑go (per step/second) | 👥 AWS operations teams — ✨ native AWS automation & org‑scale targeting |
| AWS CloudFormation | Declarative stacks, change sets, stack sets, registry & hooks | ★★★★ — first‑class AWS provisioning | 💰 No separate charge for AWS::* resource provisioning | 👥 AWS architects & infra teams — ✨ native resource support & stack sets |
| Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager | Terraform‑based GCP managed execution (Cloud Build), state in Cloud Storage | ★★★★ — GCP‑native managed Terraform | 💰 Charged via Cloud Build minutes & Storage usage | 👥 GCP teams — ✨ managed Terraform execution & blueprints |
| Azure Bicep (and ARM Templates) | Bicep DSL → ARM, VS Code tooling, what‑if previews | ★★★★ — free, native Azure tooling | 💰 Free to use; no external state required for Azure | 👥 Azure teams — ✨ simpler ARM authoring & first‑class Azure support |
Final Thoughts
Navigating the expansive landscape of cloud infrastructure automation tools can feel like charting a complex, ever-shifting map. We've explored a wide spectrum of solutions, from the foundational infrastructure as code (IaC) giants like Terraform and CloudFormation to sophisticated management platforms such as Spacelift and env0, and specialized tools like Ansible for configuration management. Each tool offers a unique philosophy and set of capabilities designed to solve specific challenges in the cloud-native ecosystem.
The core takeaway is that there is no single "best" tool; the ideal choice is deeply intertwined with your organization's specific context. Your existing technology stack, team skill set, operational maturity, and strategic goals are the primary drivers in this decision-making process. The right tool isn't just about features; it's about finding a solution that integrates seamlessly into your workflow, empowers your engineers, and delivers tangible business value through efficiency, reliability, and cost control.
A successful automation strategy often involves a layered approach. For instance, your foundational layer might be built with Terraform to provision core resources, while Ansible handles fine-grained configuration. A platform like Spacelift could then provide the governance and policy enforcement to manage it all at scale. This layered model highlights a critical point: the best cloud infrastructure automation tools are those that work well together. When evaluating options, prioritize strong API support, extensive provider ecosystems, and flexible integration capabilities.
Ultimately, the goal is to build a resilient, efficient, and cost-effective cloud environment. The powerful cloud infrastructure automation tools we've covered provide the means to achieve this, transforming infrastructure management from a manual, error-prone task into a strategic, software-driven discipline. Specialized solutions like Server Scheduler play a crucial role by complementing IaC tools, ensuring that the infrastructure you provision doesn't lead to uncontrolled spending by automatically shutting down non-production resources. Your next step is to start small, experiment with a pilot project, and build a toolchain that empowers your team to innovate faster and more reliably.