10 Essential AWS Cost Management Best Practices

Navigating the complexities of Amazon Web Services (AWS) often feels like a balancing act between unlocking its immense power and controlling its equally immense potential for cost overruns. A single misconfigured service or a fleet of idle development instances can quickly escalate your monthly bill, transforming a powerful asset into a significant financial liability. Effective AWS cost management is not just about cutting expenses; it's a strategic discipline that ensures every dollar spent on the cloud delivers maximum value, enhances operational efficiency, and supports sustainable growth. Without a proactive approach, organizations risk significant budget waste, hindering their ability to innovate and scale effectively.
Ready to capture the low-hanging fruit of cloud savings? Server Scheduler provides a powerful, agentless solution to automate the scheduling of your EC2 and RDS instances, helping you implement one of the most effective aws cost management best practices in minutes. Stop paying for idle resources and start your journey to a more cost-efficient cloud by visiting Server Scheduler today.
This article provides a comprehensive roundup of the most impactful AWS cost management best practices tailored for DevOps, FinOps, and engineering teams. We will move beyond generic advice to offer actionable strategies, practical implementation details, and real-world scenarios you can apply immediately. You will learn how to master everything from automated resource scheduling and precise right-sizing to sophisticated tagging strategies and the strategic use of Savings Plans and Reserved Instances. By the end of this guide, you will have a robust framework for taking control of your AWS spending, eliminating waste, and aligning your cloud infrastructure costs directly with your business objectives.
Contents
- Resource Scheduling and Automated Start/Stop Operations
- Right-Sizing Resources Based on Actual Utilization
- Implement Comprehensive Cost Monitoring and Tagging Strategy
- Optimize Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
- Leverage Spot Instances for Interruptible and Batch Workloads
- Implement Automated Cleanup and Resource Lifecycle Management
- Monitor and Optimize Database Instance Types and Storage
- Develop a Cross-Functional FinOps Culture and Governance
- AWS Cost Management — Best-Practice Comparison
- Related Articles
Ready to Slash Your AWS Costs?
Stop paying for idle resources. Server Scheduler automatically turns off your non-production servers when you're not using them.
Resource Scheduling and Automated Start/Stop Operations
One of the most effective AWS cost management best practices is to simply turn off resources when they are not in use. This concept, known as resource scheduling, involves implementing automated start/stop operations for non-production environments. By powering down resources like EC2 instances, RDS databases, and ElastiCache clusters during off-hours, weekends, and holidays, you can eliminate charges for idle compute capacity without manual intervention. This strategy is especially impactful for development, staging, and QA environments, which often sit unused outside of standard business hours yet accrue costs 24/7. By creating time-based schedules, organizations can achieve significant cost reductions, often between 30-70%, while ensuring infrastructure is fully operational when needed. You can learn more about implementing scheduling for your EC2 instances on serverscheduler.com.
Right-Sizing Resources Based on Actual Utilization
Another cornerstone of AWS cost management best practices is right-sizing, the process of aligning your resource specifications with their actual performance requirements. Many teams over-provision resources out of caution, leading to significant waste. Right-sizing involves analyzing key performance metrics like CPU, memory, and network utilization over time to identify and eliminate this waste by selecting more appropriate instance types or sizes. This strategy is highly effective because it directly targets paying for unused capacity. By continuously monitoring and adjusting resources to match workload demands, organizations can achieve substantial cost savings, often between 30-50%, without compromising application performance or availability. You can explore a detailed guide to safely resize your EC2 instances on serverscheduler.com.

Implement Comprehensive Cost Monitoring and Tagging Strategy
One of the most foundational AWS cost management best practices is establishing a robust and consistent tagging framework. Tagging involves attaching metadata (key-value pairs) to your AWS resources, which enables granular cost allocation and visibility. By implementing a comprehensive strategy, you can track spending by project, department, environment, or owner, transforming raw billing data into actionable business intelligence. A well-defined tagging strategy allows you to use AWS Cost Explorer and Cost Allocation Reports to their full potential. Without it, your AWS bill can become a confusing, consolidated figure that is difficult to dissect. With tags, you can pinpoint specific cost drivers, identify waste, and implement chargeback or showback models to foster a culture of cost awareness across your organization.
Pro Tip: Define 4-6 mandatory tags for all provisioned resources, such as
Environment,Owner,Project, andCostCenter. Use Service Control Policies (SCPs) and AWS CloudFormation templates to enforce tagging policies at the point of resource creation.
Optimize Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
One of the most powerful AWS cost management best practices is leveraging commitment-based pricing models like Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans. These models offer significant discounts, often up to 72%, compared to On-Demand pricing. In exchange, you commit to a consistent amount of compute usage over a one or three-year term. By analyzing historical usage data, you can identify baseline workloads that are always running, such as core production servers or essential databases. Committing this predictable portion of your usage to RIs or Savings Plans locks in a lower rate, directly reducing your hourly compute costs. This approach allows you to secure substantial savings while still using On-Demand or Spot Instances for handling variable or unpredictable demand.
Leverage Spot Instances for Interruptible and Batch Workloads
Harnessing the significant discounts offered by Spot Instances is a powerful AWS cost management best practice. These are spare EC2 compute capacity that AWS offers at discounts of up to 90% compared to On-Demand prices. The trade-off is that AWS can reclaim these instances with a two-minute warning, making them ideal for workloads that are fault-tolerant, stateless, or can handle interruptions gracefully. By strategically using Spot Instances, you can dramatically lower compute costs for a wide range of applications, including batch processing, data analysis, and non-production environments. This approach allows you to access massive computing power for a fraction of the cost, turning interruptibility into a financial advantage.
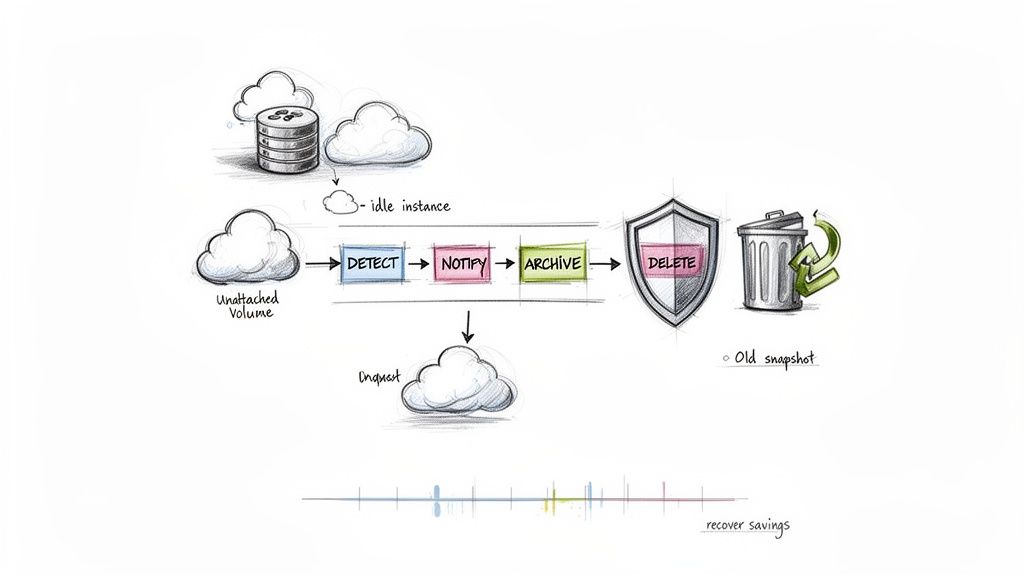
Implement Automated Cleanup and Resource Lifecycle Management
Over time, cloud environments accumulate unused, orphaned, or untagged resources that continue to incur charges despite providing no value. Implementing automated cleanup and resource lifecycle management is a crucial AWS cost management best practice that systematically identifies and terminates this digital debris. This strategy involves setting up automated scripts and lifecycle policies to detect resources like unattached EBS volumes, old snapshots, outdated AMIs, and idle Elastic IP addresses. By establishing rules for identification and removal, you can prevent this gradual cost creep and maintain a leaner, more efficient AWS environment. The savings can be immediate and substantial, directly improving your cloud ROI. You can explore a variety of cloud infrastructure automation tools to find the right fit for your stack.
Monitor and Optimize Database Instance Types and Storage
Database instances often represent a significant portion of an organization's AWS bill, making targeted optimization a high-impact cost management best practice. This involves continuously analyzing Amazon RDS performance metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, and IOPS to right-size database instances and optimize their storage configurations. By ensuring your database resources match their actual workload demands, you can prevent over-provisioning and dramatically reduce unnecessary expenditures. Optimizing database instances includes downsizing instance classes, switching to more cost-effective storage tiers, and tuning automated backup retention policies. You can learn more about the best ways for resizing your RDS instances on serverscheduler.com and discover efficient SQL query optimization techniques to further reduce load.
Develop a Cross-Functional FinOps Culture and Governance
Effective AWS cost management is not just a technical challenge; it's a cultural one. Developing a cross-functional FinOps culture means breaking down silos between engineering, finance, and operations teams to create shared ownership and accountability for cloud spending. This approach embeds cost-awareness into the entire development lifecycle, from architecture design to daily operations, transforming cost optimization from a reactive task into a proactive, continuous practice. This cultural shift relies on establishing clear governance frameworks, regular cost reviews, and transparent chargeback or showback models. Organizations that successfully adopt strong FinOps practices can achieve consistent and sustainable cost reductions by aligning cloud expenditure directly with business value. Learn more about FinOps best practices on serverscheduler.com.
AWS Cost Management — Best-Practice Comparison
| Approach | Complexity | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Scheduling | Low–Medium | 30–70% non-prod cost reduction | Non-production environments (dev, QA) |
| Right‑Sizing | Medium | 30–50% cost reduction | Long‑running, steady workloads |
| Tagging Strategy | Medium | Granular cost attribution, accountability | Orgs needing showback/chargeback |
| RIs & Savings Plans | Medium–High | Up to 72% discount | Predictable production workloads |
| Spot Instances | Medium | 70–90% savings | Batch jobs, ETL, testing |
| Automated Cleanup | Low–Medium | Recovers 10–30% wasted spend | Environments with resource sprawl |
| Database Optimization | Medium–High | 30–50% DB cost reduction | High database spend environments |
| FinOps Culture | High | Sustained 20–30% reductions | Medium-to-large organizations |